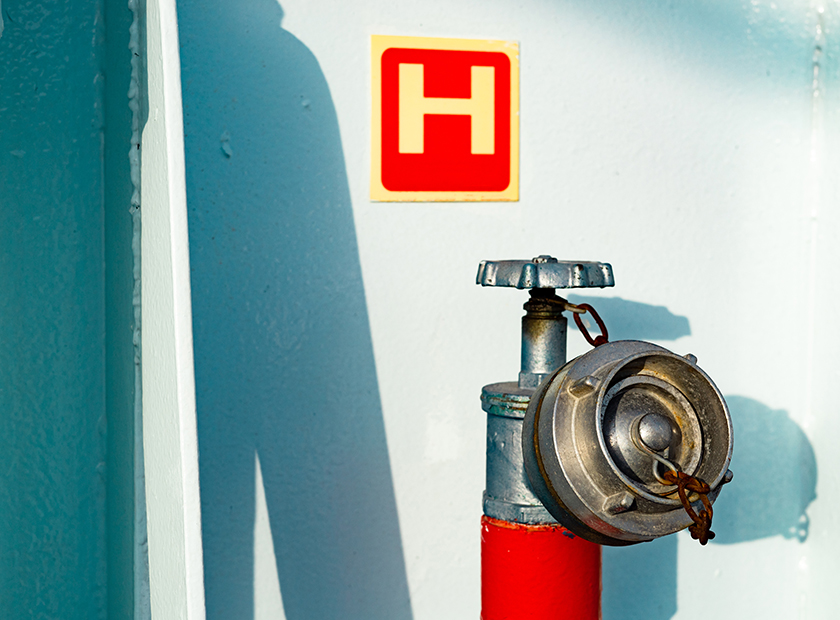
Overview
Paris and Tokyo MoUs have jointly announced a new Concentrated Inspections Campaign (CIC) that will take place from September 1st to November 30rd, 2023 with a focus on Fire Safety implementation on board ships, since high levels of deficiencies were found in recent years in this specific area. Other MoUs may also participate in the campaign which will be an additional inspection campaign to the regular PSC inspections.
Aim of CIC
The purpose of the Inspection Campaign is to determine the level of compliance with the requirements on Fire safety. Fire Safety is a key area of concern during PSC inspections. It is widely known that fire is one of the worst-case scenarios for an onboard emergency. PSC data analysis from the last five years shows that there is a lot of concern for onboard fire safety while ships have still several issues to address in this area. The PSCOs will expand their focus on the evaluation of competences of crew when performing fire drill or related emergency scenarios.
Questionnaire
The CIC questionnaire will be released in early August 2023. However, in accordance with released information, there will be a 10-question checklist covering the functionality of fire safety systems and related drills.
See Appendix A for CIC Questionnaire.
Actions required
Managers, manning offices, Officers and crew onboard should be prepared to address the PSC CiC successfully. Fire training manuals on board to be reviewed to be ship specific. Company’s superintendents to focus on onboard training during visits. Additional fire emergency scenarios to be conducted.
How we may help
SQEMARINE can provide guidance for CiC Questionnaire (Appendix A), preparing the response to questionnaire (Appendix B) and providing Fire safety Deficiency code analysis Globally (Appendix C).
Appendix A: Inspection Questionnaire
| No. | Description | Yes | No | Detention |
| 1. | Are the emergency escape routes maintained in a safe condition? | |||
| 2. | Are the fire doors maintained in good working condition? | |||
| 3. | Has the fixed fire detection and fire alarm systems, been periodically tested in accordance with the requirements of the Administration? | |||
| 4. | Are ventilation closing appliances capable of being closed? | |||
| 5. | Are the means of control for power ventilation of machinery spaces operable from two grouped positions? | |||
| 6. | Can each fire pump deliver at least the two required jets of water? | |||
| 7. | Are the means of control provided in a position outside the machinery space for stopping ventilation and oil transfer equipment operational? | |||
| 8. | Is the room for the fixed gas fire extinguishing medium used only for this purpose? | |||
| 9. | Are the valves used in the fire main line operational? | |||
| 10. | Where a fire drill was witnessed, was it found to be satisfactory? |
Appendix B: Best Practice Guidance on Inspection Campaign Questionnaire
1. Are the emergency escape routes maintained in a safe condition?
Emergency escape routes should be clearly marked onboard. Where applicable rope with attached safety harness to be ready for use. No obstacles to prevent free passing through emergency escape route. Crew to be familiar with the emergency routes per compartment.
2. Are the fire doors maintained in good working condition?
Fire doors to be checked for maintenance (absence of holes/penetrations etc). Check that they closed tightly. Close prevention means to be removed (except they are part of the system eg. Magnetic doors). Fire doors blocked to open position are one of the most common detainable issues.
3. Has the fixed fire detection and fire alarm systems, been periodically tested in accordance with the requirements of the Administration?
All related alarms to be checked for functioning. Bridge/Engine room/fire station alarm panels to be tested as required for auditable alarms. Maintenance and test records to be available for demonstration. SMS / PMS to include testing procedure for fixed fire detection systems and alarms. Blocked fire or smoke detectors in ship’s compartments are very dangerous and in case PSCO spots them, the ship will be detained.
4. Are ventilation closing appliances capable of being closed?
Check all fire dampers and ventilators to work as required. Appropriate marking to be colored to show open and close position. Remove rust from dampers so they can close tightly. Means to close the ventilation to be checked as per ships maintenance / inspection System.
5. Are the means of control for power ventilation of machinery spaces operable from two grouped positions?
Check operational status of control for power ventilation of machinery spaces. Both position systems to be checked. Apart of functionality check that there are not any closing prevention means to ventilation systems.
6. Can each fire pump deliver at least the two required jets of water?
Check equipment condition for leakages. The piping system supporting fire pumps should not have any soft patches. Check fire pumps (including emergency fire pump) for pressure. When operating in low temperature areas check fire main for icing. During fire drills check the water jet availability with one hose on the bridge and one hose in the aft deck.
7. Are the means of control provided in a position outside the machinery space for stopping ventilation and oil transfer equipment operational?
Check the operational status of means stopping ventilation and oil transfer. Quick closing valves to be free from closing preventive means. Crew to be trained to activate the stopping procedure and then reset the system to open position as required. Permanent means preventive closing vales to operate usually lead to detention. Prior entering a port these items should be checked for functionality.
8. Is the room for the fixed gas fire extinguishing medium used only for this purpose?
Check access control in the fixed gas extinguishing room. Operational step by step activation guidance should be posted next to activation control panel (for local activation). All items irrelevant to fire extinguishing system to be removed from the area.
9. Are the valves used in the fire main line operational?
Check operational status of the valves. Maintenance and inspection records to be available for review. Prior entering a port these valves should be checked for functionality.
10. Where a fire drill was witnessed, was it found to be satisfactory?
Fireman outfits and related equipment to be checked in detailed and crew should be familiar in use of them. A step-by-step drill to be performed under the supervision of Safety Officer and used as training session in order explain the reason of each step of the drill. Each crew member should know the duties and actions expected from him/her during the drill but mostly during a real time event.
Appendix C: Inspection Questionnaire
Deficiency Codes Related to Inspection Campaign
(Source RiSK4SEA)
| No. | Finding | Related PSC codes |
| 1. | Are the emergency escape routes maintained in a safe condition? | 07120 – Means of escape |
| 2. | Are the fire doors maintained in good working condition? | 03107 – Doors 07105 – Fire doors/openings in fire-resisting divisions 07101 – Fire prevention structural integrity 07103 – Division – decks, bulkheads, and penetrations |
| 3. | Has the fixed fire detection and fire alarm systems, been periodically tested in accordance with the requirements of the Administration? | 07106 – Fire detection and alarm system 07121 – Crew alarm 07108 – Ready availability of firefighting equipment 07109 – Fixed fire extinguishing installation 07110 – Firefighting equipment and appliances |
| 4. | Are ventilation closing appliances capable of being closed? | 03108 – Ventilators, air pipes, casings 07115 – Fire-dampers 07116 – Ventilation |
| 5. | Are the means of control for power ventilation of machinery spaces operable from two grouped positions? | 07116 – Ventilation 07114 – Remote Means of control (opening, pumps, ventilation, etc.) Machinery spaces |
| 6. | Can each fire pump deliver at least the two required jets of water? | 04102 – Emergency fire pump and its pipes 07113 – Fire pumps and its pipes |
| 7. | Are the means of control provided in a position outside the machinery space for stopping ventilation and oil transfer equipment operational? | 07116 – Ventilation 07122 – Fire control plan 07123 – Operation of Fire protection systems 07124 – Maintenance of Fire protection systems |
| 8. | Is the room for the fixed gas fire extinguishing medium used only for this purpose? | 07108 – Ready availability of firefighting equipment 07109 – Fixed fire extinguishing installation 07122 – Fire control plan |
| 9. | Are the valves used in the fire main line operational? | 07108 – Ready availability of firefighting equipment 07113 – Fire pumps and its pipes 07123 – Operation of Fire protection systems 07124 – Maintenance of Fire protection systems |
| 10. | Where a fire drill was witnessed, was it found to be satisfactory? | 04109 – Fire drills 07122 – Fire control plan 07125 – Evaluation of crew performance (fire drills) |
Analysis of Fire Safety related Deficiency Codes
Last 36 Months (July 2020 – June 2023) Global Statistics
(Source RiSK4SEA)
| Global Rank | Def. Code |
Deficiency Code Description | Deficiency Area |
# of Det. Defs |
# of NON Det. Defs | Total Defs | Share on overall Defs |
| 1 | 07105 | Fire doors/openings in fire-resisting divisions | Fire Safety | 416 | 7,206 | 7,622 | 2.37% |
| 8 | 07110 | Firefighting equipment and appliances | Fire Safety | 177 | 3,849 | 4,026 | 1.25% |
| 10 | 07199 | Other (fire safety) | Fire Safety | 139 | 3,731 | 3,870 | 1.20% |
| 11 | 07106 | Fire detection and alarm system | Fire Safety | 465 | 3,364 | 3,829 | 1.19% |
| 24 | 07109 | Fixed fire extinguishing installation | Fire Safety | 318 | 2,454 | 2,772 | 0.86% |
| 29 | 07115 | Fire-dampers | Fire Safety | 413 | 2,076 | 2,489 | 0.77% |
| 33 | 07108 | Ready availability of firefighting equipment | Fire Safety | 100 | 2,067 | 2,167 | 0.67% |
| 39 |
07111 | Personal equipment for fire safety | Fire Safety | 94 | 1,889 | 1,983 | 0.62% |
| 41 |
07116 | Ventilation | Fire Safety | 210 | 1,755 | 1,965 | 0.61% |
| 47 |
07113 | Fire pumps and its pipes | Fire Safety | 309 | 1,543 | 1,852 | 0.58% |
| 48 | 07120 | Means of escape | Fire Safety | 132 | 1,680 | 1,812 | 0.56% |
| 54 | 07114 | Remote Means of control (opening, pumps, ventilation, etc.) Machinery spaces | Fire Safety | 301 | 1,412 | 1,713 | 0.53% |
| 57 | 04102 | Emergency fire pump and its pipes | Emergency Systems | 388 | 1,282 | 1,670 | 0.52% |
| 63 | 04109 | Fire drills | Emergency Systems | 291 | 1,159 | 1,450 | 0.45% |
| 64 | 07126 | Oil accumulation in engine room | Fire Safety | 142 | 1,299 | 1,441 | 0.45% |
| 82 | 07101 | Fire prevention structural integrity | Fire Safety | 88 | 1,067 | 1,155 | 0.36% |
| 88 | 07117 | Jacketed high-pressure lines and oil leakage alarm | Fire Safety | 116 | 942 | 1,058 | 0.33% |
| 92 |
07122 | Fire control plan | Fire Safety | 24 | 1,004 | 1,028 | 0.32% |
| 101 |
07125 | Evaluation of crew performance (fire drills) | Fire Safety | 222 | 720 | 942 | 0.29% |
| 106 |
07124 | Maintenance of Fire protection systems | Fire Safety | 45 | 885 | 930 | 0.29% |
| 137 | 07123 | Operation of Fire protection systems | Fire Safety | 62 | 598 | 660 | 0.21% |
| 160 | 07103 | Division – decks, bulkheads, and penetrations | Fire Safety | 46 | 507 | 553 | 0.17% |
| 161 | 07112 | Emergency Escape Breathing Device and disposition | Fire Safety | 32 | 521 | 533 | 0.17% |
| 180 | 07118 | International shore-connection | Fire Safety | 8 | 452 | 460 | 0.14% |
| 294 | 07102 | Inert gas system | Fire Safety | 12 | 186 | 178 | 0.06% |
| 434 | 07107 | Fire patrol | Fire Safety | 2 | 37 | 39 | 0.01% |
| 456 | 07104 | Main Vertical zone | Fire Safety | – | 32 | 32 | 0.01% |
| 518 |
07121 | Crew alarm | Fire Safety | 2 | 11 | 13 | 0.005% |
HIghlights
- DC 07105 – Fire doors/openings in fire-resisting divisions is the most common DC the last 36M worldwide with a share of 2.37% in 321794 deficiencies. It is also responsible for 416 detentions
- Almost all Fire Safety related codes are responsible for detentions L36M
- DC 04102- Emergency fire pump and its pipes and 04109- Fire drills are not categorized in Fire Safety Deficiency Area however they are directly related to fire safety.
Interested to receive Port Call Risk Assessment to prepare your ship for the forthcoming port call?